Mobile networks
| (42 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | |||
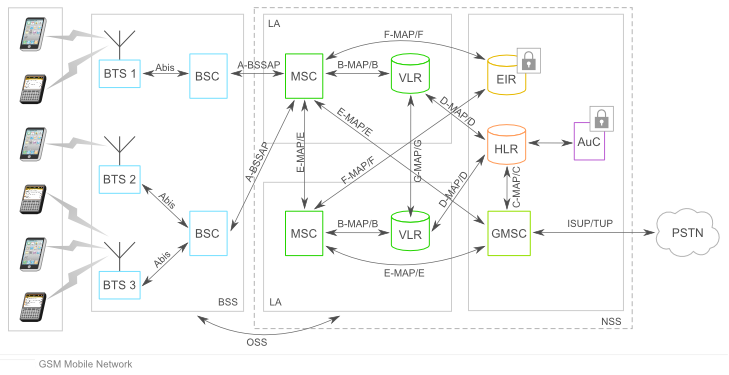
| + | GSM Mobile networks consist of mobile stations, base stations, communication links, switching center(s) and network databases which can be linked to other systems and networks as you can see in the schema below: | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[file:mobile_networks.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
A mobile network is composed by the following parts: | A mobile network is composed by the following parts: | ||
| − | + | {| | |
| − | + | |style="font-size:10px;vertical-align:top;padding-left;10px;padding-right:68px;"| | |
| − | + | '''MS''' - Mobile Station<br> | |
| − | + | '''BTS''' - Base Station<br> | |
| + | '''BSC''' - Base station Controller<br> | ||
| + | '''BSS''' - Base station subsystem | ||
| + | |style="font-size:10px;vertical-align:top;padding-right:10px;"| | ||
| + | '''MSC''' - Mobile Switching Center<br> | ||
| + | '''VLR''' - Visitor Location Register<br> | ||
| + | '''LA''' - Local Area<br> | ||
| + | '''BSSAP''' - BSS Aplication Part protocol | ||
| + | |style="font-size:10px;vertical-align:bottom;"| | ||
| + | '''HLR''' - Home Location Visitor<br> | ||
| + | '''AuC''' - Authentication Center<br> | ||
| + | '''GSMC''' - Gateway Mobile Switching Center<br> | ||
| + | '''PSTN''' - Public Switched Telephony Network<br> | ||
| + | '''EIR''' - Equipment Identity Register | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | '''Um, Abis,A-G-interfaces''' between the various<br>components of the network<br> | ||
| + | '''MAP B-G Subsets''' of Mobile Application Part Protocol<br> | ||
| + | '''ISUP''' - ISDN User Part Protocol<br> | ||
| + | '''NSS''' - Network and Switching Subsystem | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | Mobile Station (MS) | + | |
| + | |||
| + | ====Mobile Station (MS):==== | ||
* the mobile equipment (Ex: phone) | * the mobile equipment (Ex: phone) | ||
* the SIM (Subscriber identity Module) card that uniquely identified the card by the IMSI (International Mobile Subscriber Identity). | * the SIM (Subscriber identity Module) card that uniquely identified the card by the IMSI (International Mobile Subscriber Identity). | ||
| − | The base station subsystem | + | |
| + | ====The base station subsystem (BSS):==== | ||
* base station (BTS) - it defines a cell in the network | * base station (BTS) - it defines a cell in the network | ||
| − | * base station controller (BSC) - controls a group of BTSs | + | * base station controller (BSC) - controls a group of BTSs. Does handoffs, frequency hoppings, exchange functions and power control over each managed BTS |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ====The network and switching subsystem(NSS)==== | ||
| + | * Home location register (HLR) | ||
| + | ** holds all subscribers in a network. | ||
| + | ** keeps subscriber specific information like MSISDN, IMSI, current location of the MS, roaming restrictions, additional features. | ||
| + | ** there is only one HLR per network | ||
| + | * Authentication Center (AuC) | ||
| + | ** handles the authentications and encryption in a network. | ||
| + | ** it is typically located with the HLR | ||
| + | * Equipment inquiry register (EIR) | ||
| + | ** tracks of handsets on the network using the International Mobile Equipment Identity (IMEI). | ||
| + | ** there is only one EIR per network. | ||
| + | ** It is composed of three lists. The white list, the gray list, and the black list. | ||
| + | * Mobile switching center (MSC) | ||
| + | ** handles call routing, call setup, and basic switching functions. | ||
| + | ** does inter BSC handoffs and coordinates inter MSC handoffs | ||
| + | * Gateway Mobile Switching Center (GMSC) | ||
| + | ** type of MSC that is a gateway between two networks | ||
| + | ** is is used when sending a call from a subscriber to the PSTN | ||
| + | * Visitor location register (VLR) | ||
| + | ** is associated a local area(LA). | ||
| + | ** Keeps information similar to the one in the HLR for the users in it's current local area | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====The Operation and Support Subsystem==== | ||
| + | Connects the components between the NSS and the BSC, in order to control and monitor the GSM system. It is also in charge of controlling the traffic load of the BSS. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ====Interfaces==== | ||
| + | As seen in the above schema the components communicate on various interfaces. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Interface A uses BSSAP while interfaces B-G use various MAP subsets.The GMSC sends the calls to PSTN using ISUP | ||
| + | |||
| + | For more informations about the the interfaces and the protocol operating at each layer please see: | ||
| + | |||
| + | http://www.ss7-training.net/sigtran-training/ch12lev1sec2.html | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ====References and links with additional information==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | http://www0.cs.ucl.ac.uk/staff/t.pagtzis/wireless/gsm/arch.html | ||
| + | |||
| + | http://gsmfordummies.com/architecture/arch.shtml | ||
| + | |||
| + | http://www.ss7-training.net/sigtran-training/ch12lev1sec1.html | ||
Latest revision as of 12:52, 20 March 2013
GSM Mobile networks consist of mobile stations, base stations, communication links, switching center(s) and network databases which can be linked to other systems and networks as you can see in the schema below:
A mobile network is composed by the following parts:
|
MS - Mobile Station |
MSC - Mobile Switching Center |
HLR - Home Location Visitor |
Contents |
[edit] Mobile Station (MS):
- the mobile equipment (Ex: phone)
- the SIM (Subscriber identity Module) card that uniquely identified the card by the IMSI (International Mobile Subscriber Identity).
[edit] The base station subsystem (BSS):
- base station (BTS) - it defines a cell in the network
- base station controller (BSC) - controls a group of BTSs. Does handoffs, frequency hoppings, exchange functions and power control over each managed BTS
[edit] The network and switching subsystem(NSS)
- Home location register (HLR)
- holds all subscribers in a network.
- keeps subscriber specific information like MSISDN, IMSI, current location of the MS, roaming restrictions, additional features.
- there is only one HLR per network
- Authentication Center (AuC)
- handles the authentications and encryption in a network.
- it is typically located with the HLR
- Equipment inquiry register (EIR)
- tracks of handsets on the network using the International Mobile Equipment Identity (IMEI).
- there is only one EIR per network.
- It is composed of three lists. The white list, the gray list, and the black list.
- Mobile switching center (MSC)
- handles call routing, call setup, and basic switching functions.
- does inter BSC handoffs and coordinates inter MSC handoffs
- Gateway Mobile Switching Center (GMSC)
- type of MSC that is a gateway between two networks
- is is used when sending a call from a subscriber to the PSTN
- Visitor location register (VLR)
- is associated a local area(LA).
- Keeps information similar to the one in the HLR for the users in it's current local area
[edit] The Operation and Support Subsystem
Connects the components between the NSS and the BSC, in order to control and monitor the GSM system. It is also in charge of controlling the traffic load of the BSS.
[edit] Interfaces
As seen in the above schema the components communicate on various interfaces.
Interface A uses BSSAP while interfaces B-G use various MAP subsets.The GMSC sends the calls to PSTN using ISUP
For more informations about the the interfaces and the protocol operating at each layer please see:
http://www.ss7-training.net/sigtran-training/ch12lev1sec2.html
[edit] References and links with additional information
http://www0.cs.ucl.ac.uk/staff/t.pagtzis/wireless/gsm/arch.html
http://gsmfordummies.com/architecture/arch.shtml
http://www.ss7-training.net/sigtran-training/ch12lev1sec1.html